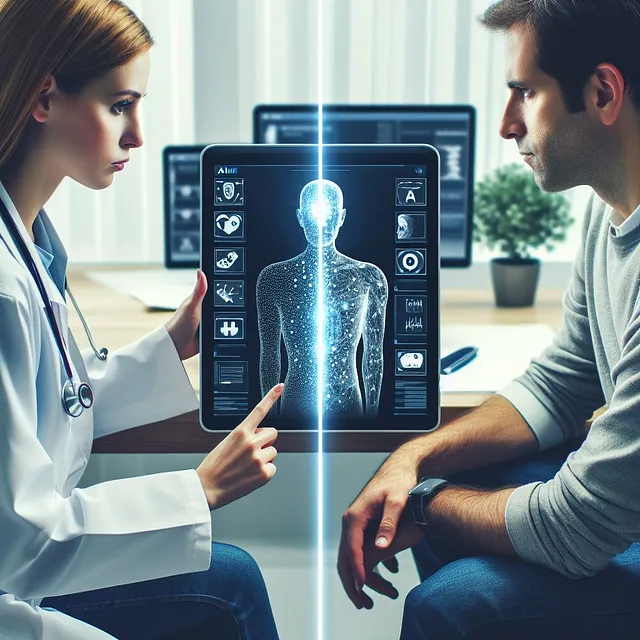
Imagine a patient who visits your clinic frequently–a complex case with chronic conditions.
With each visit, their file grows thicker, filled with prescriptions, lab reports, and handwritten notes.
Searching for that one important detail is like looking for a single needle in a giant pile of hay.

It’s a common challenge in India’s traditional paper-based system, but there’s a solution Electronic Medical Records (EMRs)
Electronic Medical Records (EMR) make this possible, revolutionizing the way healthcare is delivered.
Electronic Medical Records (EMRs)
EMRs are digital versions of a patient’s paper charts, including medical history, medications, allergies, diagnosis, treatment plans, immunization dates, and more.
They offer numerous benefits, including reduced errors, improved patient care, and cost savings.
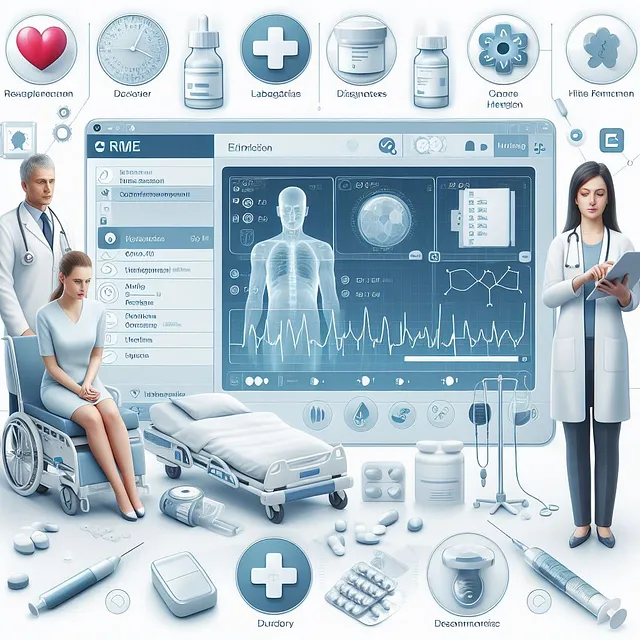

AI-powered EMRs offer a numerous benefits like Personalized Medicine, Early Disease Detection etc.,. Click the below link to learn about the benefits.
But, the critical question is, how popular are EMRs in India, and what are the challenges in their adoption?
EMRs In India
EMR adoption in India is still in its emerging stages, with a long way to go.
According to a Straits Research report, the EHR (Electronic Health Records) market, including EMR, in India, was valued at $125.4 million in 2019 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 13.2% during the forecast period (2020–2027).
Despite this, the penetration of EMRs remains low, especially in rural areas.
Global Market Size and Growth of EMR
The Global EMR market is booming. In 2023, it’s estimated to be worth around US$ 17.6 billion. Projections indicate growth of US$ 32.3 billion by 2033 showing the increasing worldwide recognition of EMR’s importance.
Indian Market Size and Growth
India’s EMR market is mirroring this upward trajectory. increasing from US$211.059 million in 2021 to US$320.069 million in 2028. displaying a CAGR of 6.13%. This signifies a positive shift within the Indian healthcare landscape.
Market Growth Drivers
Government Initiatives:
India’s focus on healthcare digitization, including the National Health Stack and Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Account (ABHA), are strong catalysts for EMR adoption.
Rising Chronic Diseases:
The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases pushes healthcare providers towards efficient records management, making EMRs attractive.
Focus on Efficiency:
EMRs streamline workflows, reduce errors, and promote greater overall healthcare efficiency.
Technological Advancements:
Cloud-based EMRs, AI-powered clinical support, and integration with other health technologies continually enhance the appeal and user experience.
Adoption rate of EMRs
- According to a report, 96% of acute care hospitals in the US had adopted at least a basic EHR system. Similarly, in the UK, 97% of general practitioners use EMR systems.
- As per reports, the EMR adoption rate in India was just 15% in 2018(approx.). This is significantly lower than the other developed countries.
- Even now only 35% of Indian hospitals currently utilize EMR systems, compared to over 90% in countries like the US and the UK.
However, despite the growth, India’s EMR adoption rate still lags behind developed nations. This gap can be attributed to various factors.
Barriers in EMR
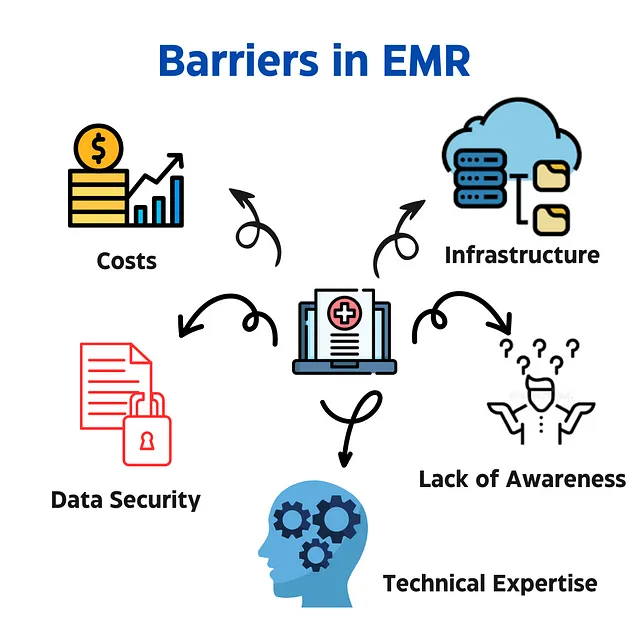
Cost:
Implementing and maintaining EMR systems can be expensive, especially for smaller clinics and hospitals.
Data Security:
Concerns about data privacy and security can deter healthcare providers from adopting EMRs.
Technical Expertise:
A lack of trained professionals to manage and utilize EMRs effectively can hinder adoption.
Infrastructure:
Limited access to reliable internet connectivity in rural areas presents a significant hurdle.
Lack of Awareness:
Many healthcare providers, particularly in smaller facilities, lack sufficient awareness about the full scope of benefits and functionalities offered by EMRs.
Benefits of EMRs
Improved patient care:
EMRs facilitate easier access to complete medical histories, enabling informed clinical decision-making and improved treatment quality.
Enhanced efficiency:
EMRs streamline workflows, reduce administrative tasks, and improve appointment scheduling, leading to better time management.
Reduced errors:
EMRs minimize data entry errors, improving the accuracy of medical records and reducing the risk of medication errors.
Better patient engagement:
Secure patient portals within EMRs empower patients to access their health information, fostering patient engagement and collaboration.
Some Major Players in India’s EMR Landscape
Conclusion
EMRs are not yet mainstream in India, but they represent a crucial step towards a more efficient, accurate, and patient-centric healthcare system.
Addressing existing challenges and leveraging government initiatives will be key to unlocking the full potential of EMRs and revolutionizing healthcare in India.